Quickly Deploy CertD with Docker and Automatically Obtain Free Wildcard SSL Certificates
Publish: 2024-08-08 | Modify: 2024-08-09
Recently, various cloud service providers have shortened the validity period of free DV SSL certificates from one year to three months. In contrast, Let's Encrypt has long supported free wildcard SSL certificates and multi-domain SSL certificates, with a validity period of three months as well. Since both have the same validity period, it is obviously more sensible and reasonable to choose the wildcard SSL certificate provided by Let's Encrypt.
For users familiar with using acme.sh, this tool can automatically apply for and renew wildcard SSL certificates, greatly simplifying the operation process. Recently, Xiaoz discovered a new tool called CertD, which can be seen as a web version of acme.sh, providing a more convenient user interface. Next, I will demonstrate how to quickly deploy CertD via Docker to apply for a free wildcard SSL certificate.

Features of CertD
- Fully automated certificate application (supports domains registered through various means such as Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, Huawei Cloud, Cloudflare, etc.)
- Fully automated certificate deployment and updates (currently supports deployment to hosts, Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, etc.)
- Supports wildcard domains/wildcard SSL, supports multiple domains on a single certificate
- Email notifications
- Provides private deployment to ensure security
- Free
Deploying CertD with Docker
Next, I will use the Docker Compose tool to privately deploy CertD. If you are not familiar with this, you need to learn about it first.
Create a docker-compose.yaml file with the following content:
version: '3.3'
services:
certd:
# Image # ↓↓↓↓↓ --- 1. Image version number, it is recommended to change to a fixed version number [optional]
image: registry.cn-shenzhen.aliyuncs.com/handsfree/certd:1.23.1
container_name: certd # Container name
restart: unless-stopped # Auto-restart
volumes:
# ↓↓↓↓↓ ------------------------------------------------------- 2. Database and certificate storage path, default stored in the host's /data/certd/ directory [optional]
- ./data:/app/data
- ./ssl:/data/ssl
ports: # Port mapping
# ↓↓↓↓ ----------------------------------------------------------3. If there is a port conflict, you can modify the first 7001 to another non-conflicting port number [optional]
- "7001:7001"
dns:
# If you encounter errors like getaddrinfo ENOTFOUND, you can try modifying or commenting out the dns configuration
- 223.5.5.5
- 223.6.6.6
- 8.8.8.8
- 8.8.4.4
environment: # Environment variables
- TZ=Asia/Shanghai
- certd_system_resetAdminPassword=false
- certd_cron_immediateTriggerOnce=false
- VITE_APP_ICP_NO=1.23.1: is the version number of CertD, you can also change it tolatest./data: local mount directory for persisting CertD data, you can change it to an absolute path./ssl: directory for exporting SSL certificates, this is added by the author
Then use the command docker-compose up -d to start the container, and access it via http://your_server_ip:7001, with the default username and password: admin/123456. Be sure to change it after logging in.
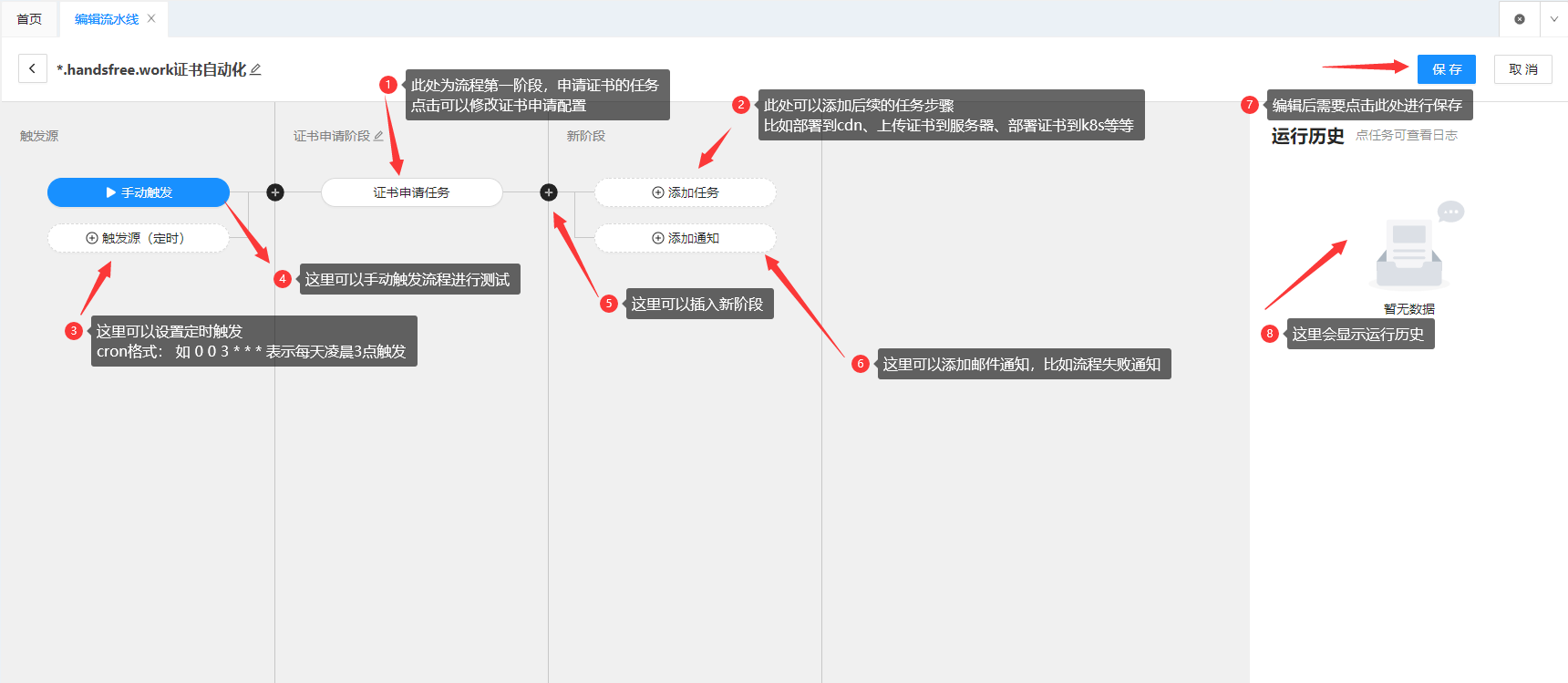
Basic Usage
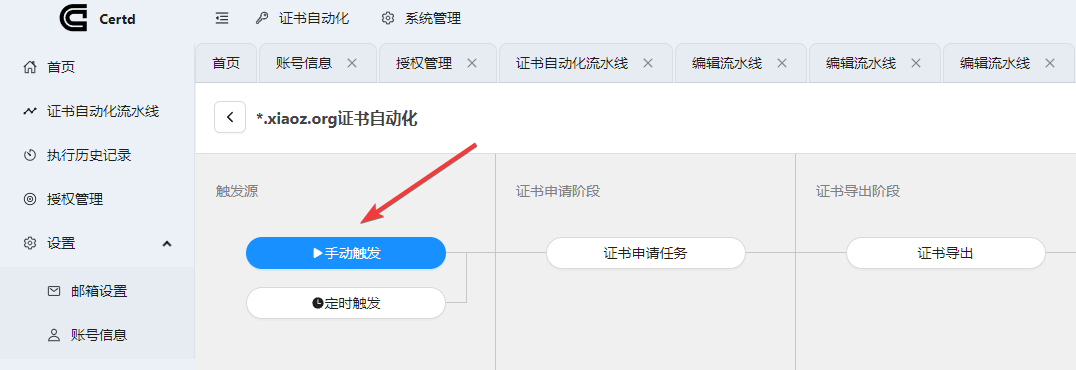
The automation process of CertD is shown in the screenshot below.
We need to first go to Authorization Management and add DNS authorization, currently supporting mainstream DNS providers such as DNSPOD, Tencent, Alibaba Cloud, Huawei Cloud, CloudFlare, etc.
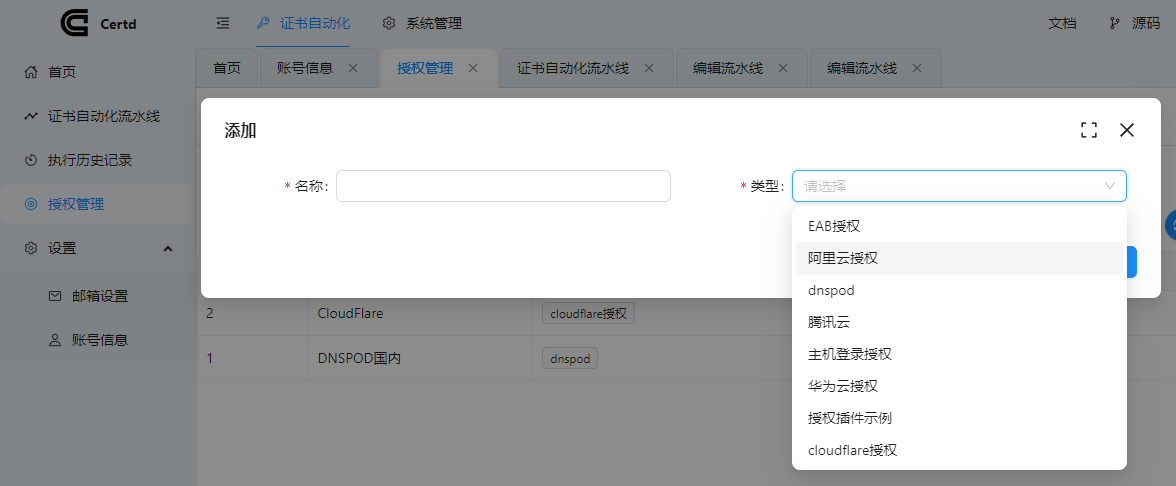
Choose the DNS provider that your domain uses!
Next, add the Certificate Automation Pipeline, filling in the required information such as domain name and email according to your situation.
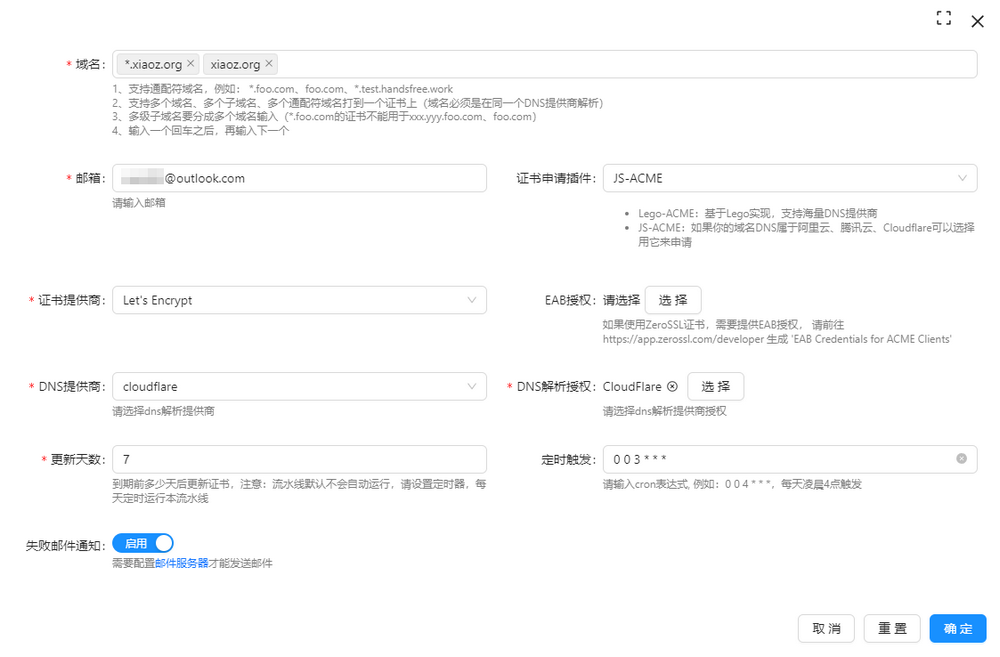
- Domain: If you need a wildcard certificate, you can fill in
*.xxx.com, and pressing the enter key can add multiple domains. Let's Encrypt supports wildcard and multi-domain, provided that these domains use the same DNS. - Certificate provider: Just select Let's Encrypt by default.
- DNS provider: Choose the one your domain uses.
- It is recommended to fill in the scheduled trigger so that it can automatically renew later, for example,
0 0 4 * * *means to check once at 4 AM every day.
Once added, if you need to immediately apply for an SSL certificate, simply click Manual Trigger. If the configuration is correct, it usually takes a few minutes to apply.
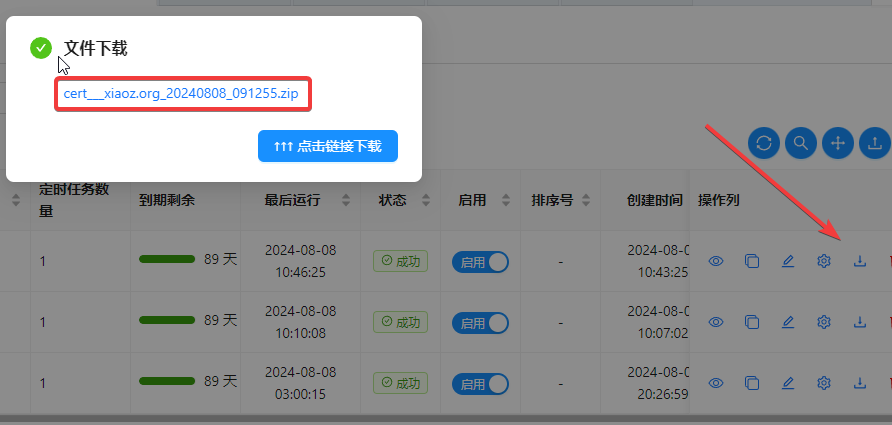
After the application is complete, click the download button to download the SSL certificate to your local machine.
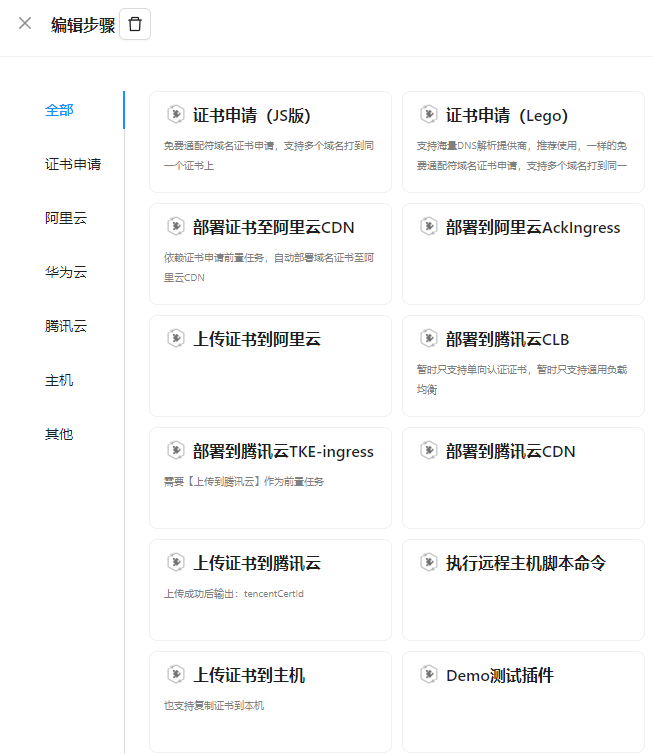
You can also manually add more steps, such as automatically exporting the certificate or uploading it to Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, etc. The automation level is quite high, although the supported providers are still relatively few.
Notes
During the application process, Xiaoz encountered a failure reason: there was a host record named _acme-challenge in the domain's DNS, conflicting with the hostname required by Let's Encrypt. Therefore, it is best to delete any existing _acme-challenge host records before applying.
Additionally, the author did not push the CertD image to Docker Hub, so you must use the Aliyun image address provided by the author above; otherwise, it cannot be pulled.
Conclusion
CertD is relatively professional and not very suitable for beginners, but it is quite suitable for operations and development personnel. Its automated certificate management process can significantly improve the efficiency of operations and developers. Currently, the number of supported service providers is limited, and we look forward to more platforms being added in the future. Thanks also to the author for their hard work.
CertD open source address: https://github.com/certd/certd
Comments

xiaoz
I come from China and I am a freelancer. I specialize in Linux operations, PHP, Golang, and front-end development. I have developed open-source projects such as Zdir, ImgURL, CCAA, and OneNav.
Random article
- DokuWiki Pseudo-Static Configuration for Nginx
- Recommended Overseas Domain Registrar: Free WHOIS Protection
- OneNav 0.9.36 Released: New Default Theme default2 Provides Ultimate Experience!
- The Process of Applying for a Free DV SSL Certificate at West.cn
- Ways to Install Office 2016 Components
- Ditto: Boosting Efficiency with Windows Clipboard Tool
- "BookStand": Your Personal Note-Taking Software with WebDAV Sync and Offline Use
- LNMP One-Click Package Causes WordPress Theme Display and Editing Issues
- What to Do If You Forget Your WordPress Username or Password?
- Sublime Text 3 Activation Code